El tokenizador BPE (Byte Pair Encoding - codificación de pares de bytes) es un algoritmo de compresión de datos que se utiliza para crear un vocabulario de subpalabras a partir de un corpus de texto. Este algoritmo se basa en la frecuencia de los pares de bytes en el texto. Se popularizó porque fue utilizado como tokenizador por LLMs como GPT, GPT-2, RoBERTa, BART y DeBERTa
Algoritmo de entrenamiento
Supongamos que tenemos un corpus de texto que solo contiene las siguientes palabras hug, pug, pun, bun y hugs, el primer paso consiste en crear un vocabulario con todos los caracteres presentes en el corpus, en nuestro caso será b, g, h, n, p, s, u
corpus_words = ["hug", "pug", "pun", "bun", "hugs"]# Concatenate all the words in the corpusinitial_corpus_tokens = ""for word in corpus_words:initial_corpus_tokens += word# Convert the concatenated string to a set of tokens to get unique tokensinitial_corpus_tokens = set(initial_corpus_tokens)print(f"Corpus words: {corpus_words}")print(f"Initial corpus tokens: {initial_corpus_tokens}")print(f"Number of initial corpus tokens: {len(initial_corpus_tokens)}")Copied
Corpus words: ['hug', 'pug', 'pun', 'bun', 'hugs']Initial corpus tokens: {'p', 'n', 'u', 's', 'h', 'g', 'b'}Number of initial corpus tokens: 7
Ahora supongamos que este es nuestro corpus de frases, es un corpus inventado, no tiene sentido
corpus = ["hug hug hug pun pun bun hugs","hug hug pug pug pun pun hugs","hug hug pug pug pun pun pun pun hugs","pug pun pun pun bun hugs","hug hug hug pun bun bun hugs",]Copied
Vamos a contar el número de veces que aparece cada palabra en el corpus, para comprobar que lo que habíamos puesto antes está bien
num_hug = 0num_pug = 0num_pun = 0num_bun = 0num_hugs = 0for sentence in corpus:words = sentence.split(" ")for word in words:if word == "hug":num_hug += 1elif word == "pug":num_pug += 1elif word == "pun":num_pun += 1elif word == "bun":num_bun += 1elif word == "hugs":num_hugs += 1print(f"Number of hug: {num_hug}")print(f"Number of pug: {num_pug}")print(f"Number of pun: {num_pun}")print(f"Number of bun: {num_bun}")print(f"Number of hugs: {num_hugs}")Copied
Number of hug: 10Number of pug: 5Number of pun: 12Number of bun: 4Number of hugs: 5
Todo lo que habíamos contado está bien, podemos seguir
Vamos a crear un diccionario con los tokens de cada palabra y el número de veces que aparece en el corpus
dict_tokens_by_word_appearance = {"hug":{"count": num_hug,"tokens": [character for character in "hug"],},"pug":{"count": num_pug,"tokens": [character for character in "pug"],},"pun":{"count": num_pun,"tokens": [character for character in "pun"],},"bun":{"count": num_bun,"tokens": [character for character in "bun"],},"hugs":{"count": num_hugs,"tokens": [character for character in "hugs"],},}dict_tokens_by_word_appearanceCopied
{'hug': {'count': 10, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g']},'pug': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'g']},'pun': {'count': 12, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'n']},'bun': {'count': 4, 'tokens': ['b', 'u', 'n']},'hugs': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 's']}}
Ahora vamos a buscar el par de tokens consecutivos que más veces aparece en el diccionario
dict_keys = dict_tokens_by_word_appearance.keys()list_consecutive_tokens = []for i, key in enumerate(dict_keys):# Get the tokens of the wordnumber_of_toneks_of_word = len(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance[key]["tokens"])# Get consecituve tokensfor j in range(number_of_toneks_of_word-1):# Get consecutive tokensconsecutive_tokens = dict_tokens_by_word_appearance[key]["tokens"][j] + dict_tokens_by_word_appearance[key]["tokens"][j+1]# Append the consecutive tokens to the list the number of times the word appearsfor _ in range(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance[key]["count"]):list_consecutive_tokens.append(consecutive_tokens)# Print the list of consecutive tokensprint(f"List of consecutive tokens: {list_consecutive_tokens}")# Get consecutive tokens with maximum frequencydict_consecutive_tokens = {}for token in list_consecutive_tokens:# Check if the token is already in the dictionaryif token in dict_consecutive_tokens:# Increment the count of the tokendict_consecutive_tokens[token] += 1# If the token is not in the dictionaryelse:# Add the token to the dictionarydict_consecutive_tokens[token] = 1# Print the dictionary of consecutive tokensprint(f"Dictionary of consecutive tokens: {dict_consecutive_tokens}")# Get the consecutive token with maximum frequencymax_consecutive_token = Nonewhile True:# Get the token with maximum frequencyconsecutive_token = max(dict_consecutive_tokens, key=dict_consecutive_tokens.get)# Check if the token is already in the list of tokensif consecutive_token in initial_corpus_tokens:# Remove token from the dictionarydict_consecutive_tokens.pop(consecutive_token)# If the token is not in the list of tokenselse:# Assign the token to the max_consecutive_tokenmax_consecutive_token = consecutive_tokenbreak# Print the consecutive token with maximum frequencyprint(f"Consecutive token with maximum frequency: {max_consecutive_token}")Copied
List of consecutive tokens: ['hu', 'hu', 'hu', 'hu', 'hu', 'hu', 'hu', 'hu', 'hu', 'hu', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'un', 'un', 'un', 'un', 'un', 'un', 'un', 'un', 'un', 'un', 'un', 'un', 'bu', 'bu', 'bu', 'bu', 'un', 'un', 'un', 'un', 'hu', 'hu', 'hu', 'hu', 'hu', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'gs', 'gs', 'gs', 'gs', 'gs']Dictionary of consecutive tokens: {'hu': 15, 'ug': 20, 'pu': 17, 'un': 16, 'bu': 4, 'gs': 5}Consecutive token with maximum frequency: ug
Hemos obtenido el par de tokens que más veces aparece. Vamos a encapsular esto en una función porque lo vamos a utilizar más veces
def get_consecutive_tokens_with_max_frequency(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance, list_corpus_tokens):dict_keys = dict_tokens_by_word_appearance.keys()list_consecutive_tokens = []for i, key in enumerate(dict_keys):# Get the tokens of the wordnumber_of_toneks_of_word = len(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance[key]["tokens"])# Get consecituve tokensfor j in range(number_of_toneks_of_word-1):# Get consecutive tokensconsecutive_tokens = dict_tokens_by_word_appearance[key]["tokens"][j] + dict_tokens_by_word_appearance[key]["tokens"][j+1]# Append the consecutive tokens to the listfor _ in range(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance[key]["count"]):list_consecutive_tokens.append(consecutive_tokens)# Get consecutive tokens with maximum frequencydict_consecutive_tokens = {}for token in list_consecutive_tokens:# Check if the token is already in the dictionaryif token in dict_consecutive_tokens:# Increment the count of the tokendict_consecutive_tokens[token] += 1# If the token is not in the dictionaryelse:# Add the token to the dictionarydict_consecutive_tokens[token] = 1# Get the consecutive token with maximum frequencymax_consecutive_token = Nonewhile True:# Get the token with maximum frequencyconsecutive_token = max(dict_consecutive_tokens, key=dict_consecutive_tokens.get)# Check if the token is already in the list of tokensif consecutive_token in list_corpus_tokens:# Remove token from the dictionarydict_consecutive_tokens.pop(consecutive_token)# If the token is not in the list of tokenselse:# Assign the token to the max_consecutive_tokenmax_consecutive_token = consecutive_tokenbreakreturn max_consecutive_tokenCopied
Comprobamos que obtenemos lo mismo que antes
max_consecutive_token = get_consecutive_tokens_with_max_frequency(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance, initial_corpus_tokens)print(f"Consecutive token with maximum frequency: {max_consecutive_token}")Copied
Consecutive token with maximum frequency: ug
Vemos que sí
Ahora nuestro corpus de tokens se puede modificar añadiendo el token ug
# new_corpus_tokens = initial_corpus_tokens + max_consecutive_tokennew_corpus_tokens = initial_corpus_tokens.copy()new_corpus_tokens.add(max_consecutive_token)print(f"Initial corpus tokens: {initial_corpus_tokens}")print(f"New corpus tokens: {new_corpus_tokens}")Copied
Initial corpus tokens: {'p', 'n', 'u', 's', 'h', 'g', 'b'}New corpus tokens: {'p', 'n', 'ug', 'g', 'b', 'u', 's', 'h'}
Metemos esto también en una función
def get_new_corpus_tokens(max_consecutive_token, initial_corpus_tokens):new_corpus_tokens = initial_corpus_tokens.copy()new_corpus_tokens.add(max_consecutive_token)return new_corpus_tokensCopied
Volveremos a comprobar que obtenemos lo mismo que antes
new_corpus_tokens = get_new_corpus_tokens(max_consecutive_token, initial_corpus_tokens)print(f"Initial corpus tokens: {initial_corpus_tokens}")print(f"New corpus tokens: {new_corpus_tokens}")Copied
Initial corpus tokens: {'p', 'n', 'u', 's', 'h', 'g', 'b'}New corpus tokens: {'p', 'n', 'ug', 'g', 'b', 'u', 's', 'h'}
Vemos que sí
Ahora vamos a modificar el diccionario en el que aparecen las palabras, los tokens y el número de veces que aparecen con el nuevo token
import copydict_keys = dict_tokens_by_word_appearance.keys()dict_tokens_by_word_appearance_tmp = copy.deepcopy(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance)for key in dict_keys:# Check if the new token is in the wordif max_consecutive_token in key:print(f"Token {max_consecutive_token} is in the word {key}")# Add the new token to the word tokensdict_tokens_by_word_appearance_tmp[key]["tokens"].append(max_consecutive_token)print(f"New tokens of the word {key}: {dict_tokens_by_word_appearance_tmp[key]['tokens']}")print(f"Initial tokens by word appearance: {dict_tokens_by_word_appearance}")print(f"New tokens by word appearance: ")dict_tokens_by_word_appearance_tmpCopied
Token ug is in the word hugNew tokens of the word hug: ['h', 'u', 'g', 'ug']Token ug is in the word pugNew tokens of the word pug: ['p', 'u', 'g', 'ug']Token ug is in the word hugsNew tokens of the word hugs: ['h', 'u', 'g', 's', 'ug']Initial tokens by word appearance: {'hug': {'count': 10, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g']}, 'pug': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'g']}, 'pun': {'count': 12, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'n']}, 'bun': {'count': 4, 'tokens': ['b', 'u', 'n']}, 'hugs': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 's']}}New tokens by word appearance:
{'hug': {'count': 10, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 'ug']},'pug': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'g', 'ug']},'pun': {'count': 12, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'n']},'bun': {'count': 4, 'tokens': ['b', 'u', 'n']},'hugs': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 's', 'ug']}}
Metemos esto en una función
def update_tokens_by_word_appearance(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance, max_consecutive_token):dict_tokens_by_word_appearance_tmp = copy.deepcopy(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance)dict_keys = dict_tokens_by_word_appearance_tmp.keys()for key in dict_keys:# Check if the new token is in the wordif max_consecutive_token in key:# Add the new token to the word tokensdict_tokens_by_word_appearance_tmp[key]["tokens"].append(max_consecutive_token)return dict_tokens_by_word_appearance_tmpCopied
Comprobamos que está bien
dict_tokens_by_word_appearance = update_tokens_by_word_appearance(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance, max_consecutive_token)print(f"New tokens by word appearance: ")dict_tokens_by_word_appearanceCopied
New tokens by word appearance:
{'hug': {'count': 10, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 'ug']},'pug': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'g', 'ug']},'pun': {'count': 12, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'n']},'bun': {'count': 4, 'tokens': ['b', 'u', 'n']},'hugs': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 's', 'ug']}}
En resumen, en una primera iteracción hemos pasado de un corpus de tokens s, g, h, u, n, p, b al nuevo corpus de tokens h, u, n, p, s, g, b, ug
Realizamos ahora una segunda iteración, obtenemos el par de tokens consecutivos que más veces aparecen en el diccionario
max_consecutive_token = get_consecutive_tokens_with_max_frequency(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance, new_corpus_tokens)print(f"Consecutive token with maximum frequency: {max_consecutive_token}")Copied
Consecutive token with maximum frequency: pu
Obtenemos el nuevo corpus de tokens
corpus_tokens = get_new_corpus_tokens(max_consecutive_token, new_corpus_tokens)print(f"Initial corpus tokens: {new_corpus_tokens}")print(f"New corpus tokens: {corpus_tokens}")Copied
Initial corpus tokens: {'p', 'n', 'ug', 'g', 'b', 'u', 's', 'h'}New corpus tokens: {'p', 'n', 'pu', 'u', 's', 'h', 'ug', 'g', 'b'}
Y obtenemos el nuevo diccionario en el que aparecen las palabras, los tokens y el número de veces que aparecen
dict_tokens_by_word_appearance = update_tokens_by_word_appearance(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance, max_consecutive_token)print(f"New tokens by word appearance: ")dict_tokens_by_word_appearanceCopied
New tokens by word appearance:
{'hug': {'count': 10, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 'ug']},'pug': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'g', 'ug', 'pu']},'pun': {'count': 12, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'n', 'pu']},'bun': {'count': 4, 'tokens': ['b', 'u', 'n']},'hugs': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 's', 'ug']}}
Ahora podemos seguir hasta tener un corpus de tokens con el tamaño que queramos, vamos a crear un corpus de 15 tokens
len_corpus_tokens = 15while len(corpus_tokens) < len_corpus_tokens:max_consecutive_token = get_consecutive_tokens_with_max_frequency(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance, corpus_tokens)print(f"Consecutive token with maximum frequency: {max_consecutive_token}")# If there are no more consecutive tokens break the loopif max_consecutive_token is None:breakcorpus_tokens = get_new_corpus_tokens(max_consecutive_token, corpus_tokens)print(f"New corpus tokens: {corpus_tokens}")dict_tokens_by_word_appearance = update_tokens_by_word_appearance(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance, max_consecutive_token)print(f"New tokens by word appearance: {dict_tokens_by_word_appearance} ")Copied
Consecutive token with maximum frequency: unNew corpus tokens: {'p', 'n', 'pu', 'un', 'u', 's', 'h', 'ug', 'g', 'b'}New tokens by word appearance: {'hug': {'count': 10, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 'ug']}, 'pug': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'g', 'ug', 'pu']}, 'pun': {'count': 12, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'n', 'pu', 'un']}, 'bun': {'count': 4, 'tokens': ['b', 'u', 'n', 'un']}, 'hugs': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 's', 'ug']}}Consecutive token with maximum frequency: huNew corpus tokens: {'p', 'hu', 'n', 'pu', 'un', 'u', 's', 'h', 'ug', 'g', 'b'}New tokens by word appearance: {'hug': {'count': 10, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 'ug', 'hu']}, 'pug': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'g', 'ug', 'pu']}, 'pun': {'count': 12, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'n', 'pu', 'un']}, 'bun': {'count': 4, 'tokens': ['b', 'u', 'n', 'un']}, 'hugs': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 's', 'ug', 'hu']}}Consecutive token with maximum frequency: gugNew corpus tokens: {'p', 'hu', 'n', 'pu', 'un', 'gug', 'u', 's', 'h', 'ug', 'g', 'b'}New tokens by word appearance: {'hug': {'count': 10, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 'ug', 'hu']}, 'pug': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'g', 'ug', 'pu']}, 'pun': {'count': 12, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'n', 'pu', 'un']}, 'bun': {'count': 4, 'tokens': ['b', 'u', 'n', 'un']}, 'hugs': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 's', 'ug', 'hu']}}Consecutive token with maximum frequency: ughuNew corpus tokens: {'p', 'hu', 'n', 'pu', 'un', 'gug', 'u', 's', 'h', 'ughu', 'ug', 'g', 'b'}New tokens by word appearance: {'hug': {'count': 10, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 'ug', 'hu']}, 'pug': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'g', 'ug', 'pu']}, 'pun': {'count': 12, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'n', 'pu', 'un']}, 'bun': {'count': 4, 'tokens': ['b', 'u', 'n', 'un']}, 'hugs': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 's', 'ug', 'hu']}}Consecutive token with maximum frequency: npuNew corpus tokens: {'p', 'hu', 'n', 'npu', 'pu', 'un', 'gug', 'u', 's', 'h', 'ughu', 'ug', 'g', 'b'}New tokens by word appearance: {'hug': {'count': 10, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 'ug', 'hu']}, 'pug': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'g', 'ug', 'pu']}, 'pun': {'count': 12, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'n', 'pu', 'un']}, 'bun': {'count': 4, 'tokens': ['b', 'u', 'n', 'un']}, 'hugs': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 's', 'ug', 'hu']}}Consecutive token with maximum frequency: puunNew corpus tokens: {'p', 'hu', 'n', 'npu', 'pu', 'un', 'gug', 'puun', 'u', 's', 'h', 'ughu', 'ug', 'g', 'b'}New tokens by word appearance: {'hug': {'count': 10, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 'ug', 'hu']}, 'pug': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'g', 'ug', 'pu']}, 'pun': {'count': 12, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'n', 'pu', 'un']}, 'bun': {'count': 4, 'tokens': ['b', 'u', 'n', 'un']}, 'hugs': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 's', 'ug', 'hu']}}
Ahora que hemos visto cómo se entrena el tokenizador BPE, vamos a entrenarlo desde cero para afianzar los conocimientos
corpus_words = ["hug", "pug", "pun", "bun", "hugs"]# Concatenate all the words in the corpusinitial_corpus_tokens = ""for word in corpus_words:initial_corpus_tokens += word# Convert the concatenated string to a set of tokens to get unique tokenscorpus_tokens = set(initial_corpus_tokens)print(f"Corpus words: {corpus_words}")print(f"Initial corpus tokens: {corpus_tokens}")print(f"Number of initial corpus tokens: {len(corpus_tokens)}")Copied
Corpus words: ['hug', 'pug', 'pun', 'bun', 'hugs']Initial corpus tokens: {'p', 'n', 'u', 's', 'h', 'g', 'b'}Number of initial corpus tokens: 7
corpus = ["hug hug hug pun pun bun hugs","hug hug pug pug pun pun hugs","hug hug pug pug pun pun pun pun hugs","pug pun pun pun bun hugs","hug hug hug pun bun bun hugs",]num_hug = 0num_pug = 0num_pun = 0num_bun = 0num_hugs = 0for sentence in corpus:words = sentence.split(" ")for word in words:if word == "hug":num_hug += 1elif word == "pug":num_pug += 1elif word == "pun":num_pun += 1elif word == "bun":num_bun += 1elif word == "hugs":num_hugs += 1dict_tokens_by_word_appearance = {"hug":{"count": num_hug,"tokens": [character for character in "hug"],},"pug":{"count": num_pug,"tokens": [character for character in "pug"],},"pun":{"count": num_pun,"tokens": [character for character in "pun"],},"bun":{"count": num_bun,"tokens": [character for character in "bun"],},"hugs":{"count": num_hugs,"tokens": [character for character in "hugs"],},}dict_tokens_by_word_appearanceCopied
{'hug': {'count': 10, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g']},'pug': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'g']},'pun': {'count': 12, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'n']},'bun': {'count': 4, 'tokens': ['b', 'u', 'n']},'hugs': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 's']}}
Lo entrenamos desde cero hasta obtener un corpus de 15 tokens
len_corpus_tokens = 15print(f"Initial corpus tokens: ({len(corpus_tokens)}) {corpus_tokens}")while len(corpus_tokens) < len_corpus_tokens:max_consecutive_token = get_consecutive_tokens_with_max_frequency(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance, corpus_tokens)# If there are no more consecutive tokens break the loopif max_consecutive_token is None:breakcorpus_tokens = get_new_corpus_tokens(max_consecutive_token, corpus_tokens)dict_tokens_by_word_appearance = update_tokens_by_word_appearance(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance, max_consecutive_token)print(f"New corpus tokens: ({len(corpus_tokens)}) {corpus_tokens}")Copied
Initial corpus tokens: (7) {'p', 'n', 'u', 's', 'h', 'g', 'b'}New corpus tokens: (15) {'p', 'hu', 'n', 'npu', 'pu', 'un', 'gug', 'puun', 'u', 's', 'h', 'ughu', 'ug', 'g', 'b'}
Tokenización
Si ahora quisiéramos tokenizar, primero tendríamos que crear un vocabulario, es decir, asignar a cada token un ID
vocab = {}for i, token in enumerate(corpus_tokens):vocab[token] = iprint(f"Vocabulary: ")vocabCopied
Vocabulary:
{'p': 0,'hu': 1,'sug': 2,'npu': 3,'ugpu': 4,'gug': 5,'u': 6,'ug': 7,'ughu': 8,'n': 9,'pu': 10,'un': 11,'puun': 12,'s': 13,'h': 14,'gs': 15,'g': 16,'b': 17}
Lo metemos en una función
def get_vocabulary(corpus_tokens):vocab = {}for i, token in enumerate(corpus_tokens):vocab[token] = ireturn vocabCopied
Comprobamos que está bien
vocab = get_vocabulary(corpus_tokens)print(f"Vocabulary: ")vocabCopied
Vocabulary:
{'p': 0,'hu': 1,'sug': 2,'npu': 3,'ugpu': 4,'gug': 5,'u': 6,'ug': 7,'ughu': 8,'n': 9,'pu': 10,'un': 11,'puun': 12,'s': 13,'h': 14,'gs': 15,'g': 16,'b': 17}
Si ahora queremos tokenizar la palabra bug podemos hacer
word = 'bug'# Get the maximum length of tokensmax_len = max(len(token) for token in vocab)print(f"Maximum length of tokens: {max_len}")# Create a empty list of tokenstokens = []while len(word) > 0:# Flag to check if the token is foundfound = False# Iterate over the maximum length of tokens from max_len to 0for i in range(max_len, 0, -1):# Get the prefix of the wordprefix = word[:i]print(f"Prefix: {prefix}")# Check if the prefix is in the vocabularyif prefix in vocab:print(f"prefix {prefix} is in the vocabulary")tokens.append(prefix)word = word[i:]found = Truebreak# if not found:# tokens.append('<UNK>')# word = word[1:]print(f"Tokens: {tokens}")Copied
Maximum length of tokens: 4Prefix: bugPrefix: bugPrefix: buPrefix: bprefix b is in the vocabularyPrefix: ugprefix ug is in the vocabularyTokens: ['b', 'ug']
Pero si ahora queremos tokenizar la palabra mug no podríamos porque el caracter m no está en el vocabulario, para ello lo tokenizamos con el token <UNK>
word = 'mug'# Get the maximum length of tokensmax_len = max(len(token) for token in vocab)print(f"Maximum length of tokens: {max_len}")# Create a empty list of tokenstokens = []while len(word) > 0:# Flag to check if the token is foundfound = False# Iterate over the maximum length of tokens from max_len to 0for i in range(max_len, 0, -1):# Get the prefix of the wordprefix = word[:i]print(f"Prefix: {prefix}")# Check if the prefix is in the vocabularyif prefix in vocab:print(f"prefix {prefix} is in the vocabulary")tokens.append(prefix)word = word[i:]found = Truebreakif not found:tokens.append('<UNK>')word = word[1:]print(f"Tokens: {tokens}")Copied
Maximum length of tokens: 4Prefix: mugPrefix: mugPrefix: muPrefix: mPrefix: ugprefix ug is in the vocabularyTokens: ['<UNK>', 'ug']
Lo metemos en una función
def tokenize_word(word, vocab):# Get the maximum length of tokensmax_len = max(len(token) for token in vocab)# Create a empty list of tokenstokens = []while len(word) > 0:# Flag to check if the token is foundfound = False# Iterate over the maximum length of tokens from max_len to 0for i in range(max_len, 0, -1):# Get the prefix of the wordprefix = word[:i]# Check if the prefix is in the vocabularyif prefix in vocab:tokens.append(prefix)word = word[i:]found = Truebreakif not found:tokens.append('<UNK>')word = word[1:]return tokensCopied
Comprobamos que está bien
print(f"Tokenization of the word 'bug': {tokenize_word('bug', vocab)}")print(f"Tokenization of the word 'mug': {tokenize_word('mug', vocab)}")Copied
Tokenization of the word 'bug': ['b', 'ug']Tokenization of the word 'mug': ['<UNK>', 'ug']
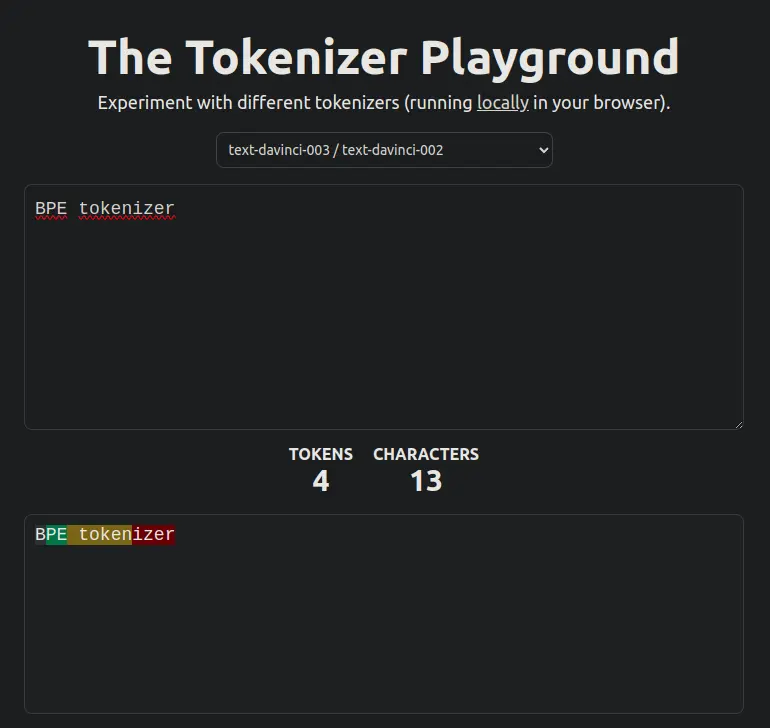
Visualizador de tokens
Ahora que sabemos cómo funciona un tokenizador BPE, vamos a ver mediante el visualizador the-tokenizer-playground cómo quedarían los tokens de cualquier sentencia