Disclaimer: This post has been translated to English using a machine translation model. Please, let me know if you find any mistakes.
The BPE (Byte Pair Encoding - byte pair encoding) algorithm is a data compression technique used to create a subword vocabulary from a text corpus. This algorithm is based on the frequency of byte pairs in the text. It gained popularity because it was used as a tokenizer by LLMs such as GPT, GPT-2, RoBERTa, BART, and DeBERTa.
Training Algorithm
Suppose we have a text corpus that only contains the following words hug, pug, pun, bun, and hugs, the first step is to create a vocabulary with all the characters present in the corpus, in our case it will be b, g, h, n, p, s, u
corpus_words = ["hug", "pug", "pun", "bun", "hugs"]# Concatenate all the words in the corpusinitial_corpus_tokens = ""for word in corpus_words:initial_corpus_tokens += word# Convert the concatenated string to a set of tokens to get unique tokensinitial_corpus_tokens = set(initial_corpus_tokens)print(f"Corpus words: {corpus_words}")print(f"Initial corpus tokens: {initial_corpus_tokens}")print(f"Number of initial corpus tokens: {len(initial_corpus_tokens)}")Copied
Corpus words: ['hug', 'pug', 'pun', 'bun', 'hugs']Initial corpus tokens: {'p', 'n', 'u', 's', 'h', 'g', 'b'}Number of initial corpus tokens: 7
Now let's assume this is our corpus of sentences; it's a made-up corpus, it doesn't make sense.
corpus = ["hug hug hug pun pun bun hugs","hug hug pug pug pun pun hugs","hug hug pug pug pun pun pun pun hugs","pug pun pun pun bun hugs","hug hug hug pun bun bun hugs",]Copied
Let's count the number of times each word appears in the corpus, to check that what we put before is correct.
num_hug = 0num_pug = 0num_pun = 0num_bun = 0num_hugs = 0for sentence in corpus:words = sentence.split(" ")for word in words:if word == "hug":num_hug += 1elif word == "pug":num_pug += 1elif word == "pun":num_pun += 1elif word == "bun":num_bun += 1elif word == "hugs":num_hugs += 1print(f"Number of hug: {num_hug}")print(f"Number of pug: {num_pug}")print(f"Number of pun: {num_pun}")print(f"Number of bun: {num_bun}")print(f"Number of hugs: {num_hugs}")Copied
Number of hug: 10Number of pug: 5Number of pun: 12Number of bun: 4Number of hugs: 5
Everything we had discussed is fine, we can continue.
Let's create a dictionary with the tokens of each word and the number of times they appear in the corpus
dict_tokens_by_word_appearance = {"hug":{"count": num_hug,"tokens": [character for character in "hug"],},"pug":{"count": num_pug,"tokens": [character for character in "pug"],},"pun":{"count": num_pun,"tokens": [character for character in "pun"],},"bun":{"count": num_bun,"tokens": [character for character in "bun"],},"hugs":{"count": num_hugs,"tokens": [character for character in "hugs"],},}dict_tokens_by_word_appearanceCopied
{'hug': {'count': 10, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g']},'pug': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'g']},'pun': {'count': 12, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'n']},'bun': {'count': 4, 'tokens': ['b', 'u', 'n']},'hugs': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 's']}}
Now we are going to find the pair of consecutive tokens that appears most frequently in the dictionary
dict_keys = dict_tokens_by_word_appearance.keys()list_consecutive_tokens = []for i, key in enumerate(dict_keys):# Get the tokens of the wordnumber_of_toneks_of_word = len(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance[key]["tokens"])# Get consecituve tokensfor j in range(number_of_toneks_of_word-1):# Get consecutive tokensconsecutive_tokens = dict_tokens_by_word_appearance[key]["tokens"][j] + dict_tokens_by_word_appearance[key]["tokens"][j+1]# Append the consecutive tokens to the list the number of times the word appearsfor _ in range(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance[key]["count"]):list_consecutive_tokens.append(consecutive_tokens)# Print the list of consecutive tokensprint(f"List of consecutive tokens: {list_consecutive_tokens}")# Get consecutive tokens with maximum frequencydict_consecutive_tokens = {}for token in list_consecutive_tokens:# Check if the token is already in the dictionaryif token in dict_consecutive_tokens:# Increment the count of the tokendict_consecutive_tokens[token] += 1# If the token is not in the dictionaryelse:# Add the token to the dictionarydict_consecutive_tokens[token] = 1# Print the dictionary of consecutive tokensprint(f"Dictionary of consecutive tokens: {dict_consecutive_tokens}")# Get the consecutive token with maximum frequencymax_consecutive_token = Nonewhile True:# Get the token with maximum frequencyconsecutive_token = max(dict_consecutive_tokens, key=dict_consecutive_tokens.get)# Check if the token is already in the list of tokensif consecutive_token in initial_corpus_tokens:# Remove token from the dictionarydict_consecutive_tokens.pop(consecutive_token)# If the token is not in the list of tokenselse:# Assign the token to the max_consecutive_tokenmax_consecutive_token = consecutive_tokenbreak# Print the consecutive token with maximum frequencyprint(f"Consecutive token with maximum frequency: {max_consecutive_token}")Copied
List of consecutive tokens: ['hu', 'hu', 'hu', 'hu', 'hu', 'hu', 'hu', 'hu', 'hu', 'hu', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'pu', 'un', 'un', 'un', 'un', 'un', 'un', 'un', 'un', 'un', 'un', 'un', 'un', 'bu', 'bu', 'bu', 'bu', 'un', 'un', 'un', 'un', 'hu', 'hu', 'hu', 'hu', 'hu', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'ug', 'gs', 'gs', 'gs', 'gs', 'gs']Dictionary of consecutive tokens: {'hu': 15, 'ug': 20, 'pu': 17, 'un': 16, 'bu': 4, 'gs': 5}Consecutive token with maximum frequency: ug
We have obtained the pair of tokens that appear most frequently. Let's encapsulate this in a function because we are going to use it more times.
def get_consecutive_tokens_with_max_frequency(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance, list_corpus_tokens):dict_keys = dict_tokens_by_word_appearance.keys()list_consecutive_tokens = []for i, key in enumerate(dict_keys):# Get the tokens of the wordnumber_of_toneks_of_word = len(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance[key]["tokens"])# Get consecituve tokensfor j in range(number_of_toneks_of_word-1):# Get consecutive tokensconsecutive_tokens = dict_tokens_by_word_appearance[key]["tokens"][j] + dict_tokens_by_word_appearance[key]["tokens"][j+1]# Append the consecutive tokens to the listfor _ in range(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance[key]["count"]):list_consecutive_tokens.append(consecutive_tokens)# Get consecutive tokens with maximum frequencydict_consecutive_tokens = {}for token in list_consecutive_tokens:# Check if the token is already in the dictionaryif token in dict_consecutive_tokens:# Increment the count of the tokendict_consecutive_tokens[token] += 1# If the token is not in the dictionaryelse:# Add the token to the dictionarydict_consecutive_tokens[token] = 1# Get the consecutive token with maximum frequencymax_consecutive_token = Nonewhile True:# Get the token with maximum frequencyconsecutive_token = max(dict_consecutive_tokens, key=dict_consecutive_tokens.get)# Check if the token is already in the list of tokensif consecutive_token in list_corpus_tokens:# Remove token from the dictionarydict_consecutive_tokens.pop(consecutive_token)# If the token is not in the list of tokenselse:# Assign the token to the max_consecutive_tokenmax_consecutive_token = consecutive_tokenbreakreturn max_consecutive_tokenCopied
We check that we get the same as before
max_consecutive_token = get_consecutive_tokens_with_max_frequency(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance, initial_corpus_tokens)print(f"Consecutive token with maximum frequency: {max_consecutive_token}")Copied
Consecutive token with maximum frequency: ug
We see that yes
Now our token corpus can be modified by adding the ug token
# new_corpus_tokens = initial_corpus_tokens + max_consecutive_tokennew_corpus_tokens = initial_corpus_tokens.copy()new_corpus_tokens.add(max_consecutive_token)print(f"Initial corpus tokens: {initial_corpus_tokens}")print(f"New corpus tokens: {new_corpus_tokens}")Copied
Initial corpus tokens: {'p', 'n', 'u', 's', 'h', 'g', 'b'}New corpus tokens: {'p', 'n', 'ug', 'g', 'b', 'u', 's', 'h'}
We also put this in a function
def get_new_corpus_tokens(max_consecutive_token, initial_corpus_tokens):new_corpus_tokens = initial_corpus_tokens.copy()new_corpus_tokens.add(max_consecutive_token)return new_corpus_tokensCopied
We will check again that we get the same as before
new_corpus_tokens = get_new_corpus_tokens(max_consecutive_token, initial_corpus_tokens)print(f"Initial corpus tokens: {initial_corpus_tokens}")print(f"New corpus tokens: {new_corpus_tokens}")Copied
Initial corpus tokens: {'p', 'n', 'u', 's', 'h', 'g', 'b'}New corpus tokens: {'p', 'n', 'ug', 'g', 'b', 'u', 's', 'h'}
We see that yes
Now we are going to modify the dictionary where the words, the tokens, and the number of times they appear are listed with the new token
import copydict_keys = dict_tokens_by_word_appearance.keys()dict_tokens_by_word_appearance_tmp = copy.deepcopy(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance)for key in dict_keys:# Check if the new token is in the wordif max_consecutive_token in key:print(f"Token {max_consecutive_token} is in the word {key}")# Add the new token to the word tokensdict_tokens_by_word_appearance_tmp[key]["tokens"].append(max_consecutive_token)print(f"New tokens of the word {key}: {dict_tokens_by_word_appearance_tmp[key]['tokens']}")print(f"Initial tokens by word appearance: {dict_tokens_by_word_appearance}")print(f"New tokens by word appearance: ")dict_tokens_by_word_appearance_tmpCopied
Token ug is in the word hugNew tokens of the word hug: ['h', 'u', 'g', 'ug']Token ug is in the word pugNew tokens of the word pug: ['p', 'u', 'g', 'ug']Token ug is in the word hugsNew tokens of the word hugs: ['h', 'u', 'g', 's', 'ug']Initial tokens by word appearance: {'hug': {'count': 10, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g']}, 'pug': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'g']}, 'pun': {'count': 12, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'n']}, 'bun': {'count': 4, 'tokens': ['b', 'u', 'n']}, 'hugs': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 's']}}New tokens by word appearance:
{'hug': {'count': 10, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 'ug']},'pug': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'g', 'ug']},'pun': {'count': 12, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'n']},'bun': {'count': 4, 'tokens': ['b', 'u', 'n']},'hugs': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 's', 'ug']}}
We put this into a function
def update_tokens_by_word_appearance(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance, max_consecutive_token):dict_tokens_by_word_appearance_tmp = copy.deepcopy(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance)dict_keys = dict_tokens_by_word_appearance_tmp.keys()for key in dict_keys:# Check if the new token is in the wordif max_consecutive_token in key:# Add the new token to the word tokensdict_tokens_by_word_appearance_tmp[key]["tokens"].append(max_consecutive_token)return dict_tokens_by_word_appearance_tmpCopied
We check that it is correct
dict_tokens_by_word_appearance = update_tokens_by_word_appearance(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance, max_consecutive_token)print(f"New tokens by word appearance: ")dict_tokens_by_word_appearanceCopied
New tokens by word appearance:
{'hug': {'count': 10, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 'ug']},'pug': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'g', 'ug']},'pun': {'count': 12, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'n']},'bun': {'count': 4, 'tokens': ['b', 'u', 'n']},'hugs': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 's', 'ug']}}
In summary, in the first iteration we have moved from a token corpus of s, g, h, u, n, p, b to the new token corpus h, u, n, p, s, g, b, ug
We now perform a second iteration, obtaining the pair of consecutive tokens that appear most frequently in the dictionary
max_consecutive_token = get_consecutive_tokens_with_max_frequency(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance, new_corpus_tokens)print(f"Consecutive token with maximum frequency: {max_consecutive_token}")Copied
Consecutive token with maximum frequency: pu
We obtain the new token corpus
corpus_tokens = get_new_corpus_tokens(max_consecutive_token, new_corpus_tokens)print(f"Initial corpus tokens: {new_corpus_tokens}")print(f"New corpus tokens: {corpus_tokens}")Copied
Initial corpus tokens: {'p', 'n', 'ug', 'g', 'b', 'u', 's', 'h'}New corpus tokens: {'p', 'n', 'pu', 'u', 's', 'h', 'ug', 'g', 'b'}
And we get the new dictionary in which the words, the tokens, and the number of times they appear are listed.
dict_tokens_by_word_appearance = update_tokens_by_word_appearance(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance, max_consecutive_token)print(f"New tokens by word appearance: ")dict_tokens_by_word_appearanceCopied
New tokens by word appearance:
{'hug': {'count': 10, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 'ug']},'pug': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'g', 'ug', 'pu']},'pun': {'count': 12, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'n', 'pu']},'bun': {'count': 4, 'tokens': ['b', 'u', 'n']},'hugs': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 's', 'ug']}}
Now we can continue until we have a corpus of tokens of the size we want, let's create a corpus of 15 tokens
len_corpus_tokens = 15while len(corpus_tokens) < len_corpus_tokens:max_consecutive_token = get_consecutive_tokens_with_max_frequency(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance, corpus_tokens)print(f"Consecutive token with maximum frequency: {max_consecutive_token}")# If there are no more consecutive tokens break the loopif max_consecutive_token is None:breakcorpus_tokens = get_new_corpus_tokens(max_consecutive_token, corpus_tokens)print(f"New corpus tokens: {corpus_tokens}")dict_tokens_by_word_appearance = update_tokens_by_word_appearance(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance, max_consecutive_token)print(f"New tokens by word appearance: {dict_tokens_by_word_appearance} ")Copied
Consecutive token with maximum frequency: unNew corpus tokens: {'p', 'n', 'pu', 'un', 'u', 's', 'h', 'ug', 'g', 'b'}New tokens by word appearance: {'hug': {'count': 10, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 'ug']}, 'pug': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'g', 'ug', 'pu']}, 'pun': {'count': 12, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'n', 'pu', 'un']}, 'bun': {'count': 4, 'tokens': ['b', 'u', 'n', 'un']}, 'hugs': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 's', 'ug']}}Consecutive token with maximum frequency: huNew corpus tokens: {'p', 'hu', 'n', 'pu', 'un', 'u', 's', 'h', 'ug', 'g', 'b'}New tokens by word appearance: {'hug': {'count': 10, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 'ug', 'hu']}, 'pug': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'g', 'ug', 'pu']}, 'pun': {'count': 12, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'n', 'pu', 'un']}, 'bun': {'count': 4, 'tokens': ['b', 'u', 'n', 'un']}, 'hugs': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 's', 'ug', 'hu']}}Consecutive token with maximum frequency: gugNew corpus tokens: {'p', 'hu', 'n', 'pu', 'un', 'gug', 'u', 's', 'h', 'ug', 'g', 'b'}New tokens by word appearance: {'hug': {'count': 10, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 'ug', 'hu']}, 'pug': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'g', 'ug', 'pu']}, 'pun': {'count': 12, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'n', 'pu', 'un']}, 'bun': {'count': 4, 'tokens': ['b', 'u', 'n', 'un']}, 'hugs': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 's', 'ug', 'hu']}}Consecutive token with maximum frequency: ughuNew corpus tokens: {'p', 'hu', 'n', 'pu', 'un', 'gug', 'u', 's', 'h', 'ughu', 'ug', 'g', 'b'}New tokens by word appearance: {'hug': {'count': 10, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 'ug', 'hu']}, 'pug': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'g', 'ug', 'pu']}, 'pun': {'count': 12, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'n', 'pu', 'un']}, 'bun': {'count': 4, 'tokens': ['b', 'u', 'n', 'un']}, 'hugs': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 's', 'ug', 'hu']}}Consecutive token with maximum frequency: npuNew corpus tokens: {'p', 'hu', 'n', 'npu', 'pu', 'un', 'gug', 'u', 's', 'h', 'ughu', 'ug', 'g', 'b'}New tokens by word appearance: {'hug': {'count': 10, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 'ug', 'hu']}, 'pug': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'g', 'ug', 'pu']}, 'pun': {'count': 12, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'n', 'pu', 'un']}, 'bun': {'count': 4, 'tokens': ['b', 'u', 'n', 'un']}, 'hugs': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 's', 'ug', 'hu']}}Consecutive token with maximum frequency: puunNew corpus tokens: {'p', 'hu', 'n', 'npu', 'pu', 'un', 'gug', 'puun', 'u', 's', 'h', 'ughu', 'ug', 'g', 'b'}New tokens by word appearance: {'hug': {'count': 10, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 'ug', 'hu']}, 'pug': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'g', 'ug', 'pu']}, 'pun': {'count': 12, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'n', 'pu', 'un']}, 'bun': {'count': 4, 'tokens': ['b', 'u', 'n', 'un']}, 'hugs': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 's', 'ug', 'hu']}}
Now that we have seen how the BPE tokenizer is trained, let's train it from scratch to reinforce our knowledge.
corpus_words = ["hug", "pug", "pun", "bun", "hugs"]# Concatenate all the words in the corpusinitial_corpus_tokens = ""for word in corpus_words:initial_corpus_tokens += word# Convert the concatenated string to a set of tokens to get unique tokenscorpus_tokens = set(initial_corpus_tokens)print(f"Corpus words: {corpus_words}")print(f"Initial corpus tokens: {corpus_tokens}")print(f"Number of initial corpus tokens: {len(corpus_tokens)}")Copied
Corpus words: ['hug', 'pug', 'pun', 'bun', 'hugs']Initial corpus tokens: {'p', 'n', 'u', 's', 'h', 'g', 'b'}Number of initial corpus tokens: 7
corpus = ["hug hug hug pun pun bun hugs","hug hug pug pug pun pun hugs","hug hug pug pug pun pun pun pun hugs","pug pun pun pun bun hugs","hug hug hug pun bun bun hugs",]num_hug = 0num_pug = 0num_pun = 0num_bun = 0num_hugs = 0for sentence in corpus:words = sentence.split(" ")for word in words:if word == "hug":num_hug += 1elif word == "pug":num_pug += 1elif word == "pun":num_pun += 1elif word == "bun":num_bun += 1elif word == "hugs":num_hugs += 1dict_tokens_by_word_appearance = {"hug":{"count": num_hug,"tokens": [character for character in "hug"],},"pug":{"count": num_pug,"tokens": [character for character in "pug"],},"pun":{"count": num_pun,"tokens": [character for character in "pun"],},"bun":{"count": num_bun,"tokens": [character for character in "bun"],},"hugs":{"count": num_hugs,"tokens": [character for character in "hugs"],},}dict_tokens_by_word_appearanceCopied
{'hug': {'count': 10, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g']},'pug': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'g']},'pun': {'count': 12, 'tokens': ['p', 'u', 'n']},'bun': {'count': 4, 'tokens': ['b', 'u', 'n']},'hugs': {'count': 5, 'tokens': ['h', 'u', 'g', 's']}}
We trained it from scratch until we obtained a corpus of 15 tokens
len_corpus_tokens = 15print(f"Initial corpus tokens: ({len(corpus_tokens)}) {corpus_tokens}")while len(corpus_tokens) < len_corpus_tokens:max_consecutive_token = get_consecutive_tokens_with_max_frequency(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance, corpus_tokens)# If there are no more consecutive tokens break the loopif max_consecutive_token is None:breakcorpus_tokens = get_new_corpus_tokens(max_consecutive_token, corpus_tokens)dict_tokens_by_word_appearance = update_tokens_by_word_appearance(dict_tokens_by_word_appearance, max_consecutive_token)print(f"New corpus tokens: ({len(corpus_tokens)}) {corpus_tokens}")Copied
Initial corpus tokens: (7) {'p', 'n', 'u', 's', 'h', 'g', 'b'}New corpus tokens: (15) {'p', 'hu', 'n', 'npu', 'pu', 'un', 'gug', 'puun', 'u', 's', 'h', 'ughu', 'ug', 'g', 'b'}
Tokenization
If we now wanted to tokenize, we would first have to create a vocabulary, that is, assign an ID to each token.
vocab = {}for i, token in enumerate(corpus_tokens):vocab[token] = iprint(f"Vocabulary: ")vocabCopied
Vocabulary:
{'p': 0,'hu': 1,'sug': 2,'npu': 3,'ugpu': 4,'gug': 5,'u': 6,'ug': 7,'ughu': 8,'n': 9,'pu': 10,'un': 11,'puun': 12,'s': 13,'h': 14,'gs': 15,'g': 16,'b': 17}
We put it in a function
def get_vocabulary(corpus_tokens):vocab = {}for i, token in enumerate(corpus_tokens):vocab[token] = ireturn vocabCopied
We check that it is correct
vocab = get_vocabulary(corpus_tokens)print(f"Vocabulary: ")vocabCopied
Vocabulary:
{'p': 0,'hu': 1,'sug': 2,'npu': 3,'ugpu': 4,'gug': 5,'u': 6,'ug': 7,'ughu': 8,'n': 9,'pu': 10,'un': 11,'puun': 12,'s': 13,'h': 14,'gs': 15,'g': 16,'b': 17}
If we now want to tokenize the word bug we can do
word = 'bug'# Get the maximum length of tokensmax_len = max(len(token) for token in vocab)print(f"Maximum length of tokens: {max_len}")# Create a empty list of tokenstokens = []while len(word) > 0:# Flag to check if the token is foundfound = False# Iterate over the maximum length of tokens from max_len to 0for i in range(max_len, 0, -1):# Get the prefix of the wordprefix = word[:i]print(f"Prefix: {prefix}")# Check if the prefix is in the vocabularyif prefix in vocab:print(f"prefix {prefix} is in the vocabulary")tokens.append(prefix)word = word[i:]found = Truebreak# if not found:# tokens.append('<UNK>')# word = word[1:]print(f"Tokens: {tokens}")Copied
Maximum length of tokens: 4Prefix: bugPrefix: bugPrefix: buPrefix: bprefix b is in the vocabularyPrefix: ugprefix ug is in the vocabularyTokens: ['b', 'ug']
But if we now want to tokenize the word mug we couldn't because the character m is not in the vocabulary, so we tokenize it with the <UNK> token.
word = 'mug'# Get the maximum length of tokensmax_len = max(len(token) for token in vocab)print(f"Maximum length of tokens: {max_len}")# Create a empty list of tokenstokens = []while len(word) > 0:# Flag to check if the token is foundfound = False# Iterate over the maximum length of tokens from max_len to 0for i in range(max_len, 0, -1):# Get the prefix of the wordprefix = word[:i]print(f"Prefix: {prefix}")# Check if the prefix is in the vocabularyif prefix in vocab:print(f"prefix {prefix} is in the vocabulary")tokens.append(prefix)word = word[i:]found = Truebreakif not found:tokens.append('<UNK>')word = word[1:]print(f"Tokens: {tokens}")Copied
Maximum length of tokens: 4Prefix: mugPrefix: mugPrefix: muPrefix: mPrefix: ugprefix ug is in the vocabularyTokens: ['<UNK>', 'ug']
We put it in a function
def tokenize_word(word, vocab):# Get the maximum length of tokensmax_len = max(len(token) for token in vocab)# Create a empty list of tokenstokens = []while len(word) > 0:# Flag to check if the token is foundfound = False# Iterate over the maximum length of tokens from max_len to 0for i in range(max_len, 0, -1):# Get the prefix of the wordprefix = word[:i]# Check if the prefix is in the vocabularyif prefix in vocab:tokens.append(prefix)word = word[i:]found = Truebreakif not found:tokens.append('<UNK>')word = word[1:]return tokensCopied
We check that it is correct
print(f"Tokenization of the word 'bug': {tokenize_word('bug', vocab)}")print(f"Tokenization of the word 'mug': {tokenize_word('mug', vocab)}")Copied
Tokenization of the word 'bug': ['b', 'ug']Tokenization of the word 'mug': ['<UNK>', 'ug']
Token Viewer
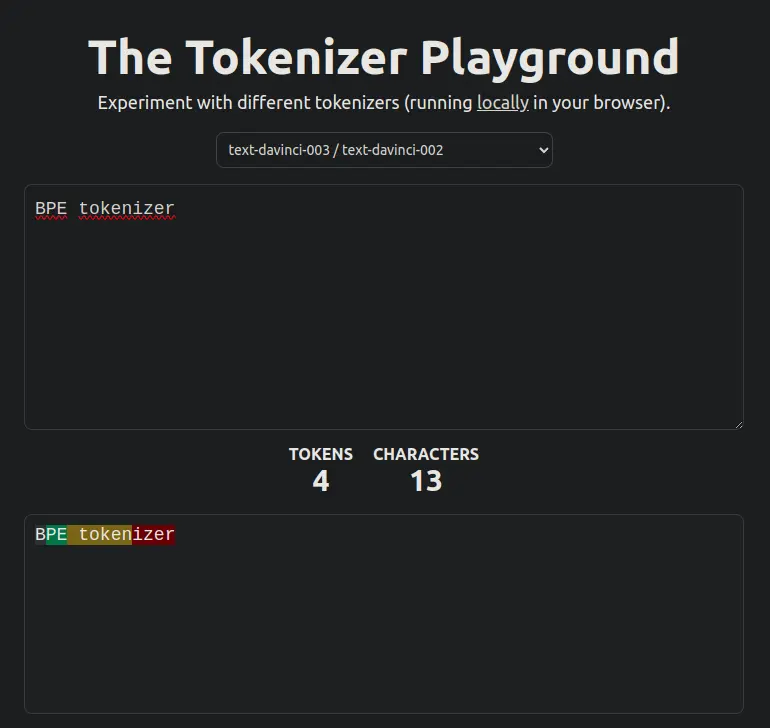
Now that we know how a BPE tokenizer works, let's see using the visualizer the-tokenizer-playground what the tokens of any sentence would look like.